CBN Benefits, Uses, Side Effects, and How Does it Effect Sleep
What is CBN? A Comprehensive Guide
If you've been asking yourself 'What is CBN' or wondering how you may incorporate cannabinol into your sleep routine, the following guide is meant for you! Slumber incorporates cannabinol, CBN, into products such as sleep gummies, CBN tinctures for sleep, and CBD gummies for sleep, so we feel particularly inclined to help others better understand cannabinol, its therapeutic benefits, how CBN is extracted from hemp plants, how CBN can be used to achieve better sleep, and introduce you to the cannabinoid that has helped many people with sleep.
In our guide to CBN you'll learn how to shop for products like hemp gummies and CBN oil, so you can make informed purchasing decisions. It is important that your sources of health and wellness products are reputable, use safe manufacturing practices, and also prioritize customers by publishing reports like Certificates of Analyses for public consumption. Additionally, we outline potential side effects of using CBN, compare those side effects with traditional sleep aids like melatonin, and we'll share personal experiences from actual CBN users so that you can hear directly from actual users of CBN products. Keep reading to discover all there is to know about CBN and its promising properties.
High-level CBN Overview
- Extracted from the hemp plant
- Non-psychoactive
- Known for sleep benefits*
- Legal in all US States
What is CBN and Where Does it Come From
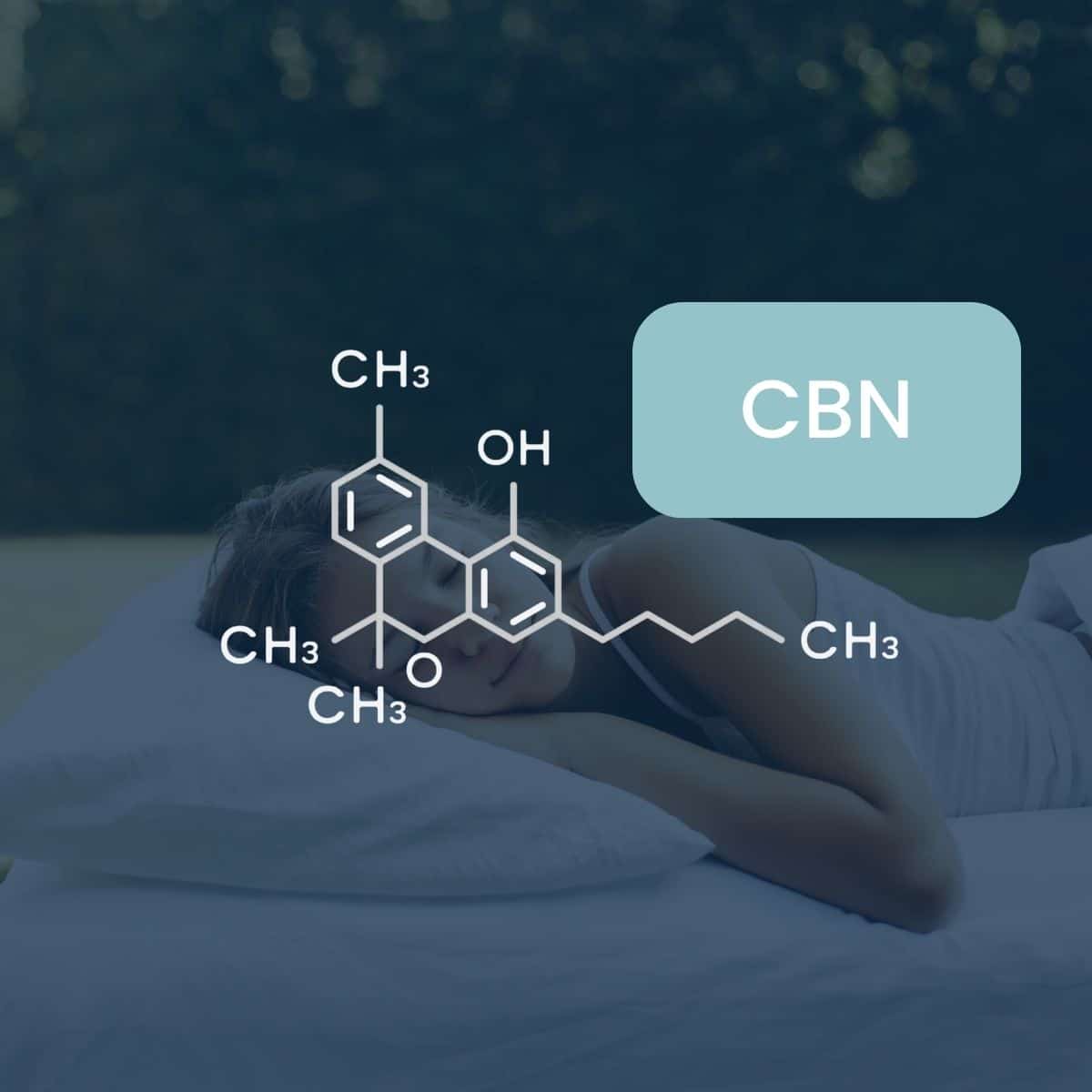
Cannabinol (CBN) is a compound found in the cannabis plant that is gaining popularity for its potential health benefits. CBN, a minor cannabinoid derived from the cannabis plant, is gaining attention for its potential health benefits and therapeutic properties. It is commonly found in aged or oxidized cannabis products. That's to say that CBN will form as oxygen and time are exposed to raw cannabis products. In order to extract CBN in a process that allows for public consumption, like the CBN products available from Slumber, there is a detailed, scientific, and hyper-controlled extraction process that needs to take place. Before we get too far into the extraction process, let's talk a little more about CBN's benefits and where it comes from.
Benefits of CBN
Studies suggest that CBN may have sleep-inducing and pain-relieving effects, as it interacts with the body's endocannabinoid system. Incorporating CBN into your wellness routine, through products like gummies, oil and tinctures, or capsules could potentially aid in pain management. The combined benefits of CBN vary widely from person to person as each of our biochemsitry and phsyciological makeup is unique. The benefits reported here and in further detail in this guide are based on customer testimonials, consumer sleep studies conducted in partnership with a 3rd party, international peer-reviewed journal articles, and reputable sources in the United States covering cannabinol and the benefits of CBN.
Brief History of CBN
CBN was first identified back in 1896, making it one of the first cannabinoids to be isolated. In the 1940s, researchers began studying CBN's potential sedative and sleep-enhancing effects. Over time, scientists learned that CBN is produced when THC degrades.
By the 1990s, CBN's abilities to reduce pain and inflammation were recognized. Recently, improved extraction has made pure CBN widely available. As of 2022, over 120 different cannabinoids have been identified, but CBN remains one of the most promising for therapeutic applications as well as within over the counter options. Many people in the United States are currently relying on cannabinoids like CBN for serving them as a sleep aid, a supplemental mitigator of stress and anxiety, to help reduce physical soreness, and many other applications.
Ongoing research continues to uncover new medical benefits of CBN, like reducing anxiety, stimulating appetite, and neuroprotection. The future is bright for this versatile cannabinoid as both an effective supplement and valuable component of the entourage effect. Slumber is committed to publishing all of our available CBN research so that more people can have access to a promising compound as well as data to support (or not) its efficacy.
CBN Extraction for CBN Gummies, CBN Oils, and CBN Products
To understand CBN is to know the process that takes place to ultimately arrive to a publicly consumable product. CBN can be consumed in a few different formats and it does occur naturally in cannabis. That's not to say that CBN is cannabis, but that cannabis has naturally occurring CBN and in various concentrations after a process of aging occurs. But how does a compound found in cannabis go from a psychoactive carrier plant to a non-psychoactive sleep aid that is consumed by the public?
The CBN Oil Manufacturing & Extraction Process
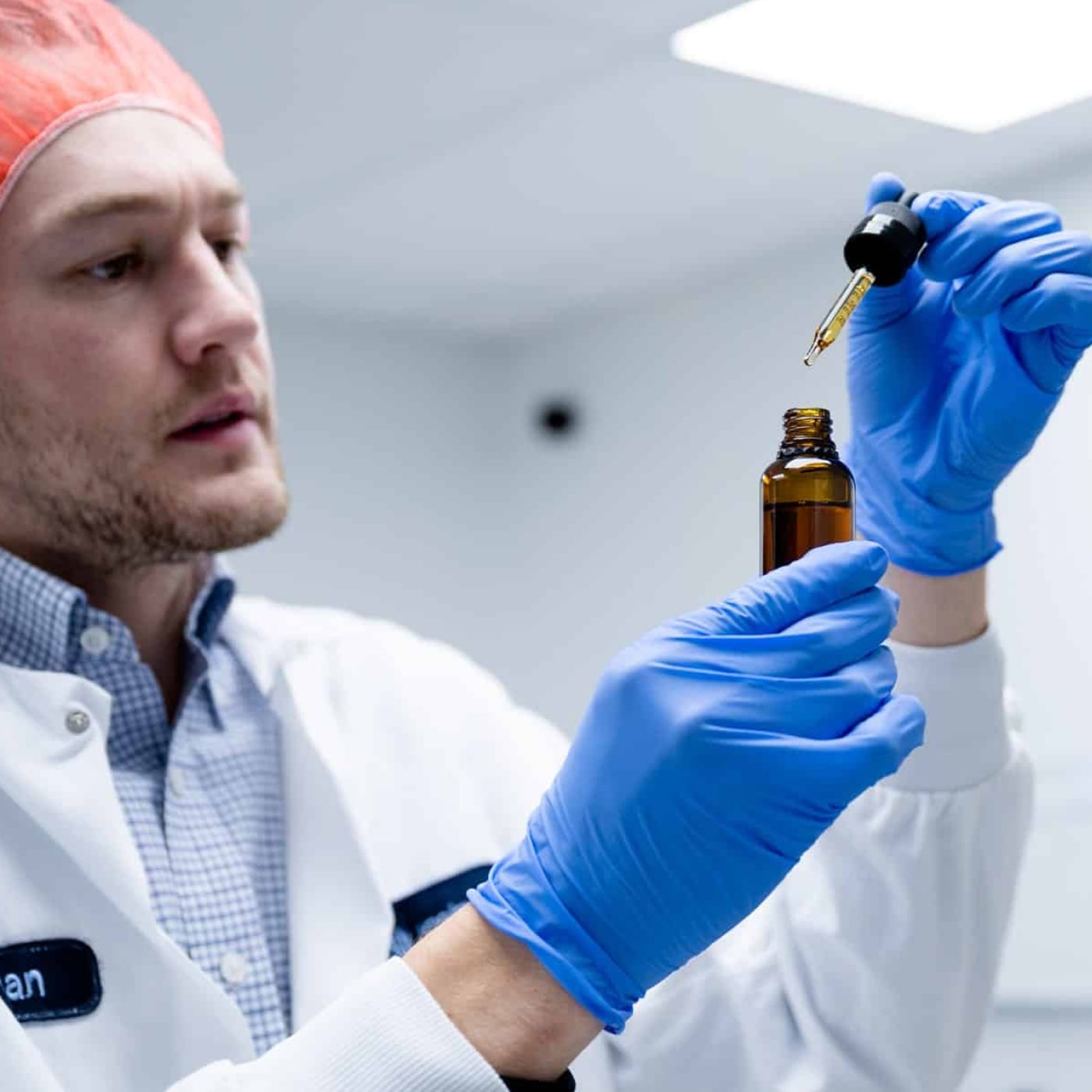
To start, the process all begins with raw source material in the form of aged cannabis plants, high CBN strains of cannabis, or materials with a high amount of naturally occurring CBN. This source material needs to endure a drying and aging process before it can be used to extract CBN. Over time and as the cannabis plant is exposed to air and ages, THC converts to CBN, which is how the process of extracting CBN oil begins. Sometimes, the dried cannabis plants that are rich with CBN are exposed to heat in a process called decarboxylation to activate the compounds. In the case of CBN, that process may not be involved in all products available for public consumption. The reason for that is because of the aging and drying process which naturally activates CBN.
There are multiple ways for the extraction process to occur in order to derive CBN oil from raw materials. Below are 3 steps involved in that process along with variations in the process to illustrate the variety of ways CBN is extracted:
1. Initial Extraction: The primary extraction can be done using either solvent extraction methods employing substances like ethanol or butane, or this process can occur via CO2 extraction. The latter is recognized for its safety and efficacy, ensuring that no residual solvents remain in the end product. At Slumber, CO2 extraction is the preferred method, aligning with the industry's best practices to guarantee a safe and effective product.
2. Purification: Following extraction, purification steps such as winterization are carried out. Winterization involves mixing the raw oil with alcohol and freezing it to segregate undesired components like fats and waxes and extract them from the material. The mix is then filtered, and the ethanol is evaporated, leaving behind a more concentrated cannabinoid extract. Slumber adheres to this standard purification procedure to ensure the integrity and quality of the CBN extract.
3. Distillation: The final refinement occurs through distillation, where heat is applied to vaporize cannabinoids, which are then collected in a concentrated form. This phase aids in increasing the CBN concentration further, ensuring a high-quality product ready for formulation into CBN oil.
Each of these stages is crucial in adhering to industry standards and regulations, ensuring the production of high-quality CBN oil that's ready for various wellness applications. As a company, Slumber is committed to meeting or exceeding industry standards, policies, and guidelines for extraction and manufacturing of CBN products. The people who are using CBN to help aid their lives deserve products that are supremely high quality, effective, clean, and deliver on their promise.
How CBN Extraction Differs from CBD
Though the extraction processes for CBN and CBD share similarities, there are key distinctions rooted in the nature of these two cannabinoids and their presence in the cannabis plant:
-
Base Material:
CBN: Derived from the aging and oxidation of THC, typically found in aged cannabis.
CBD: Extracted from hemp plants bred to be high in CBD and low in THC, without the need for an aging process. -
Extraction:
Both CBN and CBD can be extracted using solvent or CO2 extraction methods. However, the yields for CBD are generally higher due to its abundant presence in hemp, unlike CBN which requires the aging of THC-rich cannabis. Slumber utilizes the CO2 extraction method for both CBN and CBD to ensure maximum safety and efficacy. -
Purification and Distillation:
The steps involved in purification and distillation are relatively similar for both CBN and CBD, aiming to remove unwanted compounds and further concentrate the cannabinoids. Slumber follows these standard processes to ensure the purity and concentration of the cannabinoids in their products.
The distinct origins and abundance of CBN and CBD in the cannabis plant contribute to the differences in their extraction processes. While both processes aim to achieve a pure and concentrated form of the cannabinoids, the preliminary steps leading to the extraction stage vary, highlighting the unique nature of CBN and CBD extraction.
Now, having understood the extraction process, let's delve deeper into the science of how CBN interacts with our body's endocannabinoid system to produce its effects.
The Science of How CBN Works
CBN interacts with the body's endocannabinoid system (ECS) to produce its effects. Specifically, it binds to receptors CB1 and CB2 concentrated in the brain and connected to the nervous system. The cause behind all of the reported benefits of CBN exist within its relationship to the brain's receptors because they are directly connected with functions of the body. So when CBN binds to the receptors commonly associated with sleep, pain, and mood, the overall effects are a result of communication the brain is receiving from the receptors, to over-simplify the process. Below we'll go into a little more details about the scientific processes behind how CBN works:
Endocannabinoid System & Brain Receptors
While CBN has a lower binding affinity than THC, it still activates the brain's receptors and particularly CB1 and CB2. This stimulation is believed to be behind many of CBN’s therapeutic properties, as we mentioned above. The brain is receiving communication that it is tired and therefore a person feels sleepy, probably falls asleep, and assuming a healthy night of sleep, they should stay asleep. That whole process begins within the communication between the receptors and the brain. Some of the key ways that CBN interacts with receptors:
1. Binding CB1 receptors may induce the sedative effects that make CBN beneficial for sleep.
2. Activating CB2 receptors, predominantly in immune cells, may account for CBN’s potential anti-inflammatory properties.
3. CBN binds weakly to CB receptors compared to THC, so is much less likely to cause a “high”.
Research also indicates CBN may positively interact with:
- TRPV1 receptors involved in pain perception and body temperature regulation. This may underlie CBN’s analgesic and neuroprotective potential.
- Serotonin receptors related to mood and anxiety. CBN’s ability to activate these could help explain its proposed stress-relieving qualities.
While more studies are still needed, early research provides insight into the complex ways CBN may target the ECS and other receptor systems to produce its array of therapeutic effects.
Now that we've explored how CBN interacts with the body's endocannabinoid system, let's look at one of the most popular ways people are experiencing its benefits - by eating CBN gummies.
Potential Health Benefits of CBN
CBN has garnered attention for its potential health benefits because of its growing popularity among adults who are seeking a sleep aid that works for them consistently. CBN has also gained exposure because of its ever-present availability in the over the counter markets as well as online. Slumber, for example, is committed to researching the potential health benefits of CBN as reported by actual users of the product and then democratizing access to that research in order to elevate the profile of a very compelling compound. A lot of the research which has been done so far has been done on small scales within the United States or on larger scales internationally. There is certainly overlapping outcomes as it relates to the research, and when combined with customer testimonials or consumer research studies, the commonalities speak to the benefits of CBN. Here are some of the insights from research conducted on CBN:
- Reduced pain and inflammation, making it promising for pain management
- Antibacterial properties that may aid in treating infections
- Improved sleep quality, benefiting those with sleep issues
- Neuroprotective effects, making it potentially therapeutic for conditions like Parkinson's disease
A 2019 sleep study found CBN decreased anxiety and initially improved sleep in chronic pain patients. While further research is needed, CBN may offer overall wellness advantages. Specifically, CBN has demonstrated sedative effects that may promote better sleep. Studies suggest it may help reduce insomnia and improve sleep quality and duration. CBN’s sleep benefits may be due to its interaction with the endocannabinoid system and neurotransmitters. Its effects seem enhanced when combined with THC, CBD, or other cannabinoids. Individual responses to CBN’s sleep-promoting effects can vary.
With a better understanding of the promising effects of CBN, we'll look next at some of the other specific ways it may be used therapeutically.
CBN's Effect on Sleep
CBN reportedly has sedative effects which potentially aid in promoting sleep with the proper CBN dosage. It may help reduce insomnia and improve sleep duration and quality. CBN's effect on sleep may be attributed to its interaction with the endocannabinoid system and the modulation of neurotransmitter release. Research suggests that CBN's sedative properties may be enhanced when combined with other cannabinoids like THC or CBD, working alongside them in what is known as the entourage effect. Individual responses to CBN's sleep-inducing effects may vary.
Other Therapeutic Uses of CBN
CBN has demonstrated potential as an anti-inflammatory agent, which may be beneficial for conditions like arthritis. Its analgesic properties can potentially alleviate pain and discomfort. Studies have explored CBN's ability to reduce seizures in certain types of epilepsy. Additionally, CBN may stimulate appetite, making it useful for conditions involving loss of appetite or chemotherapy-induced nausea. The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has approved forms of CBD and synthetic THC for use in treating seizures, nausea, vomiting, and loss of appetite in specific situations. So far, no products containing CBN have been approved for medical use by the FDA. However, further research is needed to fully explore and validate these therapeutic applications of CBN.
CBN
CBD
Similarities and Differences Between CBN and CBD
Both CBN and CBD are cannabinoids with distinct effects on the body. CBN is produced from the degradation of THC, while CBD is derived directly from the hemp plant. CBN is known for its sedative and sleep-inducing properties, whereas CBD is recognized for its anti-inflammatory and pain-relieving effects. When comparing CBN vs CBD, the main differences between them lie in their specific properties and effects. Although both compounds offer potential health benefits, further research is required to fully understand their therapeutic uses. In certain products, CBN and CBD can be combined for enhanced benefits.
Is CBN Legal?
In accordance with the guidelines provided by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA), CBN products derived from hemp and containing less than 0.3% THC are legal to sell, distribute, and consume across all US states. While these products are legal in the US, staying informed about any changes in regulations is crucial. It's important to note:
-
The legal status of CBN differs from that of CBD and THC.
-
Compliance with local and state laws is necessary.
-
Manufacturers must understand and adhere to the legal requirements set forth in the 2018 Farm Bill for producing CBN items.
It's essential to stay updated on the legal status of CBN in your region and adhere to safety guidelines while exploring CBN products for sleep or other uses.
How to Use CBN Products Properly?
To properly use CBN products, follow the instructions on the product label and make sure to hold the manufacturer of any CBN prodicts you purchase accountable to having certificates of anlayses for all products that are available. Apprpriately using CBN and incorporating CBN into your wellness routine begins with selecting a high quality brand that you trust. When getting started with CBN products, start with a low dose and gradually increase as needed. For example, start with 1/2 of a gummy to see how the effects take hold after 45-60 minutes. If you are looking for a stronger effect then take some or all of the remaining gummy. Depending the CBN product format that you're trying, you can dose your CBN accordingly. The important thing is that you are monitoring the amount of CBN you're ingesting to make sure you find the right dosage for your individual needs. Always take CBN before bedtime, as CBN may cause drowsiness. Consult a healthcare professional if you are pregnant, breastfeeding, or have medical conditions.
Dosage Guidelines for CBN Products
Dosage guidelines for CBN products vary depending on the individual's needs and the specific product. It is generally recommended to start with a lower dosage and gradually increase if needed. Factors such as body weight, metabolism, and tolerance can also affect the appropriate CBN dosage.Each product has a supplement fact panel and suggested serving information. Carefully read the entire packaging before using the product.
Some customers have shared that they prefer a higher or lower dose depending on their sleep needs. We recommend starting with a 5-10mg dose of CBN and slowly increasing by increments of 5mg until the desired sleep effect is achieved.
To ensure safe and effective use of CBN, it is advisable to consult with a healthcare professional for personalized dosage guidance. Following recommended dosage guidelines is crucial for optimizing the benefits of CBN while minimizing the risk of potential side effects.
Side Effects and Risks of CBN
The side effects of any supplement, including CBN products can vary widely among individual use and depend on a variety of factors. Some of the factors which may impact the effects of CBN and any potential side effects include weight, stomach contents, metabolism, other medications, and generally brain chemistry. Again, there are a host of reasons why side effects can vary, and it is important to be cognizant that taking CBN may result in side effects that are desired and others that may not be your desired outcome. Dizziness, dry mouth, fatigue, and sleepiness are some of the most commonly reported side effects of taking CBN. If you experience any of these or other side effects that may be undesirable for you, please contact your healthcare provider, physician, or dial 9-1-1 if you're in an emergency. It is not very common for emergency situations to occur because of the extraction process described in this guide, if done appropriately, helps to protect against adverse effects of CBN.
It's crucial to be aware of potential interactions with medications such as blood thinners and sedatives. Long-term use may lead to tolerance and potential addiction. Before using CBN, especially if taking other medications or having underlying health conditions, it's essential to consult a healthcare provider. Additionally, avoid driving or operating heavy machinery after taking CBN, as it may impair cognitive and motor function. Remember, everyone responds differently, and the positive benefits may outweigh the side effects. If your desired side effects of CBN are reached in a healthy way, and especially if your doctor endorses your use of CBN products then you should feel comfortable with CBN, its side effects, and the minimal understood risks that exist associated with ingesting CBN and CBN products.
Who Should Not Take CBN
While early research indicates therapeutic potential, CBN may not be suitable for everyone. We want everyone to be aware of the expanded and additional risks that exist when taking a cannabinoid product, full spectrum CBN, or other products that may have an impact on your health and well-being. Here are a few examples of who should not take CBN for you to consider:
1) Pregnant or breastfeeding women
2) People with liver disease
3) Anyone with a history of drug abuse
4) People already taking sedatives, blood thinners, or other medication should check with their physician
While CBN shows promise in benefiting many people, individuals with certain medical conditions or situations should weigh the risks and consider alternatives when deciding if CBN suits their needs. When incorporating CBN into your wellness routine, it's crucial to seek reputable, high-quality products. If you keep your standards high for the type of products you put into your body then the chances for having a desired, pleasurable, or positive experience with CBN. There are many things to consider when choosing CBN, CBN products for sleep, or maybe sleep gummies for your routine. Below are a few of the things we'd like to advise you look for when purchasing CBN.
Finding Trustworthy CBN Brands and Products
Identifying reputable and trustworthy manufacturers and sellers is crucial when purchasing CBN products.
Another important factor to consider is the importance of third-party lab testing, which helps ensure the quality and safety of the products. Clear and accurate product labeling and information are also essential for making an informed purchase. Additionally, taking into account factors such as product potency, purity, and ingredients can help you choose the right CBN product for your needs.
Lastly, reading reviews and seeking recommendations from trusted sources can provide valuable insights when purchasing CBN products.
What to Look for When Buying CBN Products?
With the rise in popularity of CBN products, it is important to source them from reputable companies. Here are some tips on identifying trustworthy CBN brands:
-
Check company certifications and quality standards. Look for manufacturers that follow Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) or have certifications from organizations like NSF International. This indicates a commitment to quality and safety.
-
Review third-party lab testing. Any reputable CBN company should provide up-to-date Certificates of Analysis (COAs) from an independent lab, verifying the potency and purity of their products.
-
Research the brand reputation. Look at ratings on the Better Business Bureau (BBB) and Trustpilot to see what other customers have experienced. Favorable ratings over an extended period are a good sign.
-
Ensure transparency. Quality CBN brands openly provide information on their manufacturing process, ingredients, and contact details. Look for those committed to transparency.
-
Evaluate product selection. Companies that offer a wide variety of CBN products in various strengths and forms may invest more in product development and meeting diverse customer needs.
-
Check hemp sourcing. CBN is derived from hemp, so brands should disclose their suppliers and any efforts to ensure sustainable and high-quality hemp cultivation.
Doing thorough research enables you to find a trustworthy CBN company that offers safe, effective products through ethical business practices. Taking these key factors into account helps you make a confident purchasing decision.
Conclusion
We hope this guide provides a helpful explanation of "what is cbn" - where it comes from, how it differs from CBD, its potential uses, current research, and more. With a foundational understanding of "what is cbn", you can now assess if a CBN supplement may be worthwhile.
While more studies are still needed, early findings suggest CBN may aid conditions like insomnia, pain, and anxiety. When used properly per dosage guidelines with reputable products, CBN appears relatively low-risk for most. Based on promising research and positive anecdotal reports, CBN is worth exploring as a natural supplement for improved sleep, pain, or general wellness - through discussing any new supplement with your healthcare provider is advised. The emerging science makes CBN an intriguing option for supporting overall wellbeing.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the Base or Carrier oil used in your CBN products?
Slumber CBN used Certified Organic MCT Oil as the base/carrier oil in all of the products.
What is your method of extraction?
Slumber’s raw ingredient Cannabinol (CBN) is extracted from hemp. We use a C02 extraction method to convert into CBD isolate. From there, we have a proprietary method and conversion to get us to the finial state of CBN at a 98-99% potency level.
Where is your hemp sourced? What practices are used?
Prior to extraction, the hemp plant used in Slumber’s products comes from farms that use environmentally friendly and sustainable growing practices. The farms are located here in Colorado.
Do you run a Full Panels? How often do you test?
Slumber prioritizes getting all of proud Raw and Bulk Ingredients tested by reputable 3rd party labs.
We do Full-Panels on all of the raw ingredients and have started to incorporate them into many of our final batched products.
WE LAB TEST ALL FINAL PRODUCT BATCHES BEFORE OFFERING THEM TO OUR CUSTOMERS.
Check out our lab results here.
What is CBN and what does it do for you?
CBN is a minor cannabinoid studied for sedative qualities that may improve sleep duration and quality. It interacts with the endocannabinoid system but is not psychoactive. Research also indicates potential anti-inflammatory, pain relief, anticonvulsant and neuroprotective effects.
What is the difference between CBN and CBD?
CBN is derived from aged cannabis and known for its sedative, sleep-promoting qualities. CBD comes directly from hemp, is more extensively studied than CBN, and is known for anxiety relief, pain relief, and reducing seizures. For an in-depth CBN vs CBD comparison guide, please read our full CBN vs CBD guide.
Is CBN good for anxiety?
Early research suggests CBN may help reduce anxiety by promoting relaxation and calmness through its interaction with nervous system receptors.
Does CBN give you a buzz?
No, CBN is not known to be intoxicating or psychoactive at typical dosages, unlike THC which causes a high.
Is CBN hard on the liver?
There is limited research on CBN's effects on the liver. However, it is metabolized in the liver so those with liver disease should use caution or avoid it. It is always best to consult your medical doctor before trying any new supplement, especially if you have an underlying health condition like liver disease.