Written by Rich Barnes
Exploring the Benefits of CBD, CBN, and THC
The world of cannabinoids is vast and intriguing, often sparking curiosity and interest from seasoned researchers and the general public related to their benefits. With increasing attention on the potential therapeutic benefits of compounds like CBD (cannabidiol), CBN (cannabinol), and THC (tetrahydrocannabinol), there’s one term that has gained significant traction in recent years: The Entourage Effect.
At Slumber, we want to equip our community with as many health and wellness resources as possible. In this in-depth exploration, we’ll dive deep into the concept of the entourage effect and the compounds represented and explore the benefits of CBD, THC, and CBN using reputable sources and peer-reviewed research studies published both domestically and internationally. We hope to shed light on how each cannabinoid can benefit the general population, and when combined, it might amplify the therapeutic potential of cannabinoids.
It’s important to tell you that statements about CBD, THC, and CBN have not been reviewed by the FDA, and that any information Slumber relays to our community is not meant to diagnose, treat, or cure any disease. If you are unsure whether these compounds are right for you, please consult your primary care physician for a professional opinion.
Cannabinoids: CBD, CBN, and THC
While cannabis boasts over a hundred different cannabinoids, CBD, CBN, and THC are among the most researched and discussed. Each of them has unique characteristics that we want to lay out for you:
- CBD (Cannabidiol): Known for its potential therapeutic benefits without the intoxicating effects, CBD has been studied for its potential anti-inflammatory, anxiolytic, and neuroprotective properties. When thinking about CBD, you can qualify the potential benefits into enabling better sleep, pain and inflammation mitigation, and stress and anxiety reduction. Some of CBD’s most common form factors include tinctures and CBD gummies.
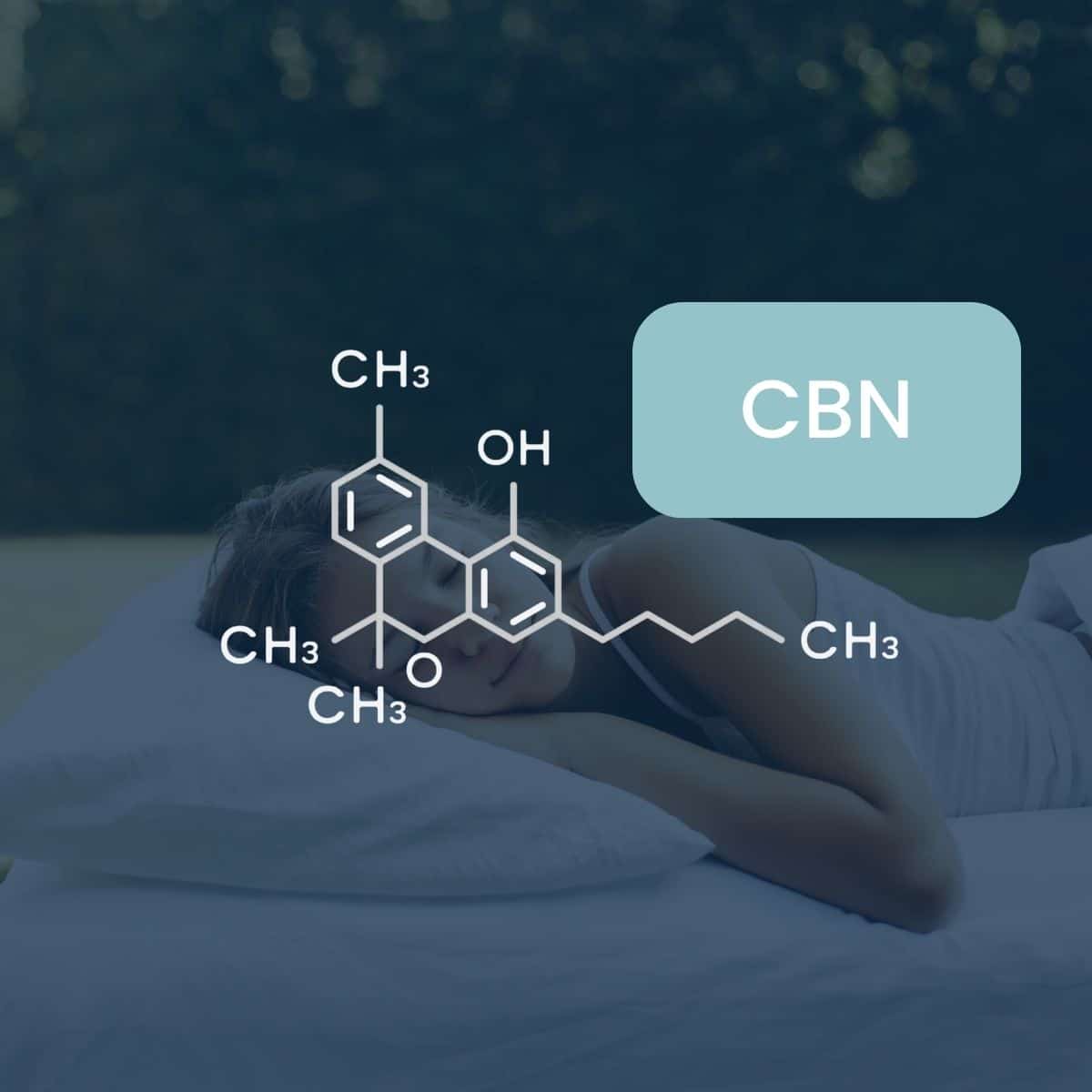
- CBN (Cannabinol): Lesser-known but equally intriguing, CBN is gaining attention for its potential sedative effects and possible benefits for sleep. CBN can come in various forms such as a tincture, gummy, and capsule.
- THC (Tetrahydrocannabinol): Famously associated with the “high” of cannabis, THC has its array of potential therapeutic effects, including pain relief and appetite stimulation. One of Slumber’s highlighted products that showcases this compound’s benefits is the Afternoon Delight – a THC gummy combined with CBD.
The Science-Backed Benefits of CBD: What the Research Tells Us
Cannabidiol (CBD), a non-intoxicating compound derived from the Cannabis sativa plant, has taken the health and wellness industry by storm in recent years. While anecdotal accounts tout a range of benefits, what does the scientific literature actually say? In this essay, we’ll dive into peer-reviewed journal articles to explore the documented benefits of CBD, shedding light on this captivating compound. Please keep in mind that we are elevating scientific studies that are published in the United States as well as internationally. Some studies use rodents and human subjects to arrive at the outcomes.
1. Potential Anti-inflammatory Properties
One of CBD’s most widely recognized benefits is its potential anti-inflammatory properties. A study published in the Journal of Experimental Medicine found that CBD significantly reduced chronic inflammation and pain in some rodents. Such findings are promising for conditions characterized by inflammation, such as arthritis or chronic pain.
1. Pain Management
2. Appetite Stimulation
3. Antiemetic Properties
4. Sleep Aid
The Potential Benefits of CBN: Exploring Initial Research
Cannabinol (CBN) may not be as widely recognized as its cannabis-derived counterparts, CBD and THC, but it's steadily gaining traction in the wellness community. Emerging from the shadows of limited research, CBN is being heralded for its unique health benefits. Let's delve into the scientific literature and peer-reviewed studies to understand CBN's therapeutic potential - our star ingredient at Slumber and the basis for our published guide to CBN.
1. Potential Sleep Aid
While often overshadowed by the more prominent cannabinoids, CBN's potential as a sleep aid has been one of its standout characteristics. Preliminary research suggests that CBN might promote longer and more restful sleep. Though more extensive studies are needed, and we will be relentlessly supporting the advancement of CBN studies, this finding positions CBN as a promising alternative for those grappling with sleep disorders.
What is the Entourage Effect?
The term "entourage effect" was first introduced in 1998 by renowned scientists Raphael Mechoulam and Shimon Ben-Shabat. It proposes that all the components present in cannabis, including cannabinoids, terpenes, and flavonoids, work better together than they do individually. It's a symphony of components harmonizing their individual effects to produce a stronger, combined result. Think of this concept as a symphony where all instruments together create a beautiful harmonic exploration of sound and space, whereas the instruments individually cannot produce that same outcome. Put another way, the entourage effect explores how each compound, when combined together, like in Slumber’s Deep Zzzs product, has the potential to create a more desirable outcome for the person in search of sleep in this example. One way we’ve shown that potential is through our sleep study.
How the Entourage Effect Amplifies Benefits
Slumber’s Commitment to Quality, Education, and Transparency
Slumber Deep Zzzs Gummies
Slumber's Deep ZZZ's gummies are expertly formulated without melatonin and 3mg THC, 25mg CBD, and 8mg CBN to promote sleep within 30-60 minutes of consumption.
Customers love the delicious lemon raspberry flavor and use of only vegan ingredients, Deep Zzz's are one of the most potent and tasty CBD sleep aids on the market.
Product Highlights
Great taste
Available online and ships to 49 states (Not Colorado)
Doctor approved and recommended
30-Day Money Back Guarantee
Save 15% OFF with Code: bettersleep
What is the Entourage Effect?
In Conclusion
The entourage effect, a harmonious interaction between cannabinoids, terpenes, and other cannabis compounds, represents the future of cannabinoid research. It underscores the idea that nature, in its wisdom, has woven a complex tapestry of compounds that, when working together, produce effects greater than the sum of their parts.
At Slumber, we remain committed to harnessing this wisdom, ensuring every product we offer resonates with the symphony of the entourage effect. Stay curious, stay informed, and trust Slumbner to be your guide in the world of cannabinoids
Written and medically reviewed by:
Dr. Jim Giltner, MD
Ophthalmologist, 36 of years of medical practice
References:
- Mechoulam, R., & Ben-Shabat, S. (1998). From gan-zi-gun-nu to anandamide and 2-arachidonoylglycerol: the ongoing story of cannabis. Natural Product Reports.
- Blessing, E. M., Steenkamp, M. M., Manzanares, J., & Marmar, C. R. (2015). Cannabidiol as a Potential Treatment for Anxiety Disorders. Neurotherapeutics.
- Russo, E. B. (2007). History of cannabis and its preparations in saga, science, and sobriquet. Chemistry & Biodiversity.
- Whiting, P. F., Wolff, R. F., Deshpande, S., Nisio, M. D., Duffy, S., Hernandez, A. V., ... & Kleijnen, J. (2015). Cannabinoids for medical use: A systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA.
- Zuardi, A. W., Hallak, J. E., & Crippa, J. A. (2012). Interaction between cannabidiol (CBD) and ∆9-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC): influence of administration interval and dose ratio between the cannabinoids. Psychopharmacology.
- Russo, E. B. (2011). Taming THC: potential cannabis synergy and phytocannabinoid‐terpenoid entourage effects. British Journal of Pharmacology.
- Baron, E. P. (2018). Medicinal properties of cannabinoids, terpenes, and flavonoids in cannabis, and benefits in migraine, headache, and pain.
Benefits of CBD References:
- Costa, B., Trovato, A. E., Comelli, F., Giagnoni, G., & Colleoni, M. (2007). The non-psychoactive cannabis constituent cannabidiol is an orally effective therapeutic agent in rat chronic inflammatory and neuropathic pain. Journal of Experimental Medicine.
- Bergamaschi, M. M., Queiroz, R. H., Chagas, M. H., de Oliveira, D. C., De Martinis, B. S., Kapczinski, F., ... & Crippa, J. A. (2011). Cannabidiol reduces the anxiety simulated public speaking induces in treatment-naïve social phobia patients. Neuropsychopharmacology.
- Schier, A. R., Ribeiro, N. P., Silva, A. C., Hallak, J. E., Crippa, J. A., Nardi, A. E., & Zuardi, A. W. (2014). Antidepressant-like and anxiolytic-like effects of cannabidiol: a chemical compound of Cannabis sativa. Journal of Chemical Neuroanatomy.
- Iuvone, T., Esposito, G., Esposito, R., Santamaria, R., Di Rosa, M., & Izzo, A. A. (2004). Neuroprotective effect of cannabidiol, a non-psychoactive component from Cannabis sativa, on β-amyloid-induced toxicity in PC12 cells. British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology.
- Devinsky, O., Cross, J. H., & Wright, S. (2017). Trial of Cannabidiol for Drug-Resistant Seizures in the Dravet Syndrome. New England Journal of Medicine.
- Oláh, A., Tóth, B. I., Borbíró, I., Sugawara, K., Szöllõsi, A. G., Czifra, G., ... & Bíró, T. (2014). Cannabidiol exerts sebostatic and antiinflammatory effects on human sebocytes.
Benefits of THC References:
- Wilsey, B., Marcotte, T., Deutsch, R., Gouaux, B., Sakai, S., & Donaghe, H. (2013). Low-dose vaporized cannabis significantly improves neuropathic pain. Journal of Pain and Symptom Management.
- Haney, M., Rabkin, J., Gunderson, E., & Foltin, R. W. (2005). Dronabinol and marijuana in HIV+ marijuana smokers: Acute effects on caloric intake and mood. Psychopharmacology.
- Parker, L. A., Rock, E. M., & Limebeer, C. L. (2011). Regulation of nausea and vomiting by cannabinoids. British Journal of Pharmacology.
- Cousens, K., & DiMascio, A. (1973). (-) Delta 9 THC as an hypnotic. An experimental study of three dose levels. Journal of Clinical Psychopharmacology.
- Fishbein-Kaminietsky, M., Gafni, M., & Sarne, Y. (2014). Ultralow doses of THC protect the brain from neuroinflammation-induced cognitive damage. Journal of Neuroscience Research.
- Merritt, J. C., Crawford, W. J., Alexander, P. C., Anduze, A. L., & Gelbart, S. S. (1980). Effect of marihuana on intraocular and blood pressure in glaucoma. Journal of the National Medical Association.
Benefits of CBN References:
- Mahadevan, A., & Siegel, C. (2009). The role of cannabinoids in sleep and wake regulation. Journal of Clinical Sleep Medicine.
- Zurier, R. B., & Burstein, S. H. (2016). Cannabinoids, inflammation, and fibrosis. European Journal of Pharmacology.
- Appendino, G., Gibbons, S., Giana, A., Pagani, A., Grassi, G., Stavri, M., Smith, E., & Rahman, M. M. (2008). Antibacterial cannabinoids from Cannabis sativa: a structure-activity study. Journal of Natural Products.
- Farrimond, J. A., Whalley, B. J., & Williams, C. M. (2012). Cannabinol and cannabidiol exert opposing effects on rat feeding patterns. Psychopharmacology.
- Hampson, A. J., Grimaldi, M., Axelrod, J., & Wink, D. (1998). Cannabidiol and (-)Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol are neuroprotective antioxidants. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.